Results of cerebral cavernous malformation surgery in patients with сavernoma-associated epilepsy
Keywords:
Cavernoma, Cavernous malformation, Epilepsy syrgery, Hemosiderin, SeizureAbstract
Objective: to present the results of surgical resection of cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) in patients with сavernoma-associated epilepsy. To assess the risk factors for an adverse outcome.
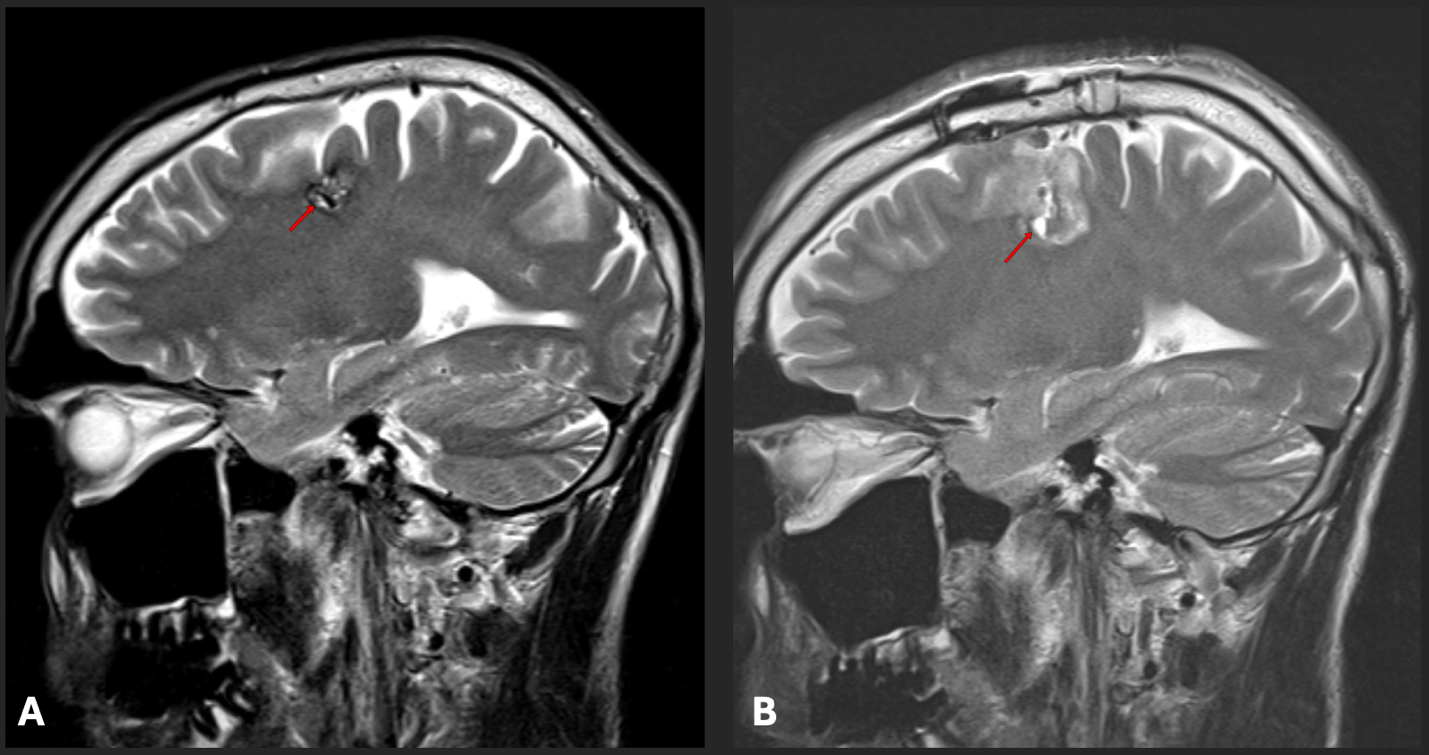
Methods: a retrospective analysis of 50 patients with supratentorial CCMs presenting epileptic seizures was performed. All patients underwent surgical CCM resection along with the hemosiderin fringe excision, except in cases when the CCM was localized in eloquent brain regions. In the first 24 hours after the surgery, patients underwent a brain MRI. The MRI study was evaluated by two independent radiologists. The radicality of the CCM and the hemosiderin ring resection around the CCM was evaluated. Long-term results were evaluated using the Engel Surgical Outcome Scale.
Results: The follow-up period was 36.5/33 (21.2; 47.8) months (Max 70.6 months, Min 11.2 months). Forty-four (88%) patients had no recurrence of seizures in the postoperative period. Additionally, 30 (68.2%) of them stopped taking anticonvulsants completely. Four (8%) patients achieved Engel class II outcome (rare seizures remained), and in 2 (4%) of patients, the dynamics in seizure frequency after surgery was not observed. An analysis of the factors influencing the outcome demonstrated that only the radical removal of the hemosiderin ring statistically confirmed its significance in relieving seizures (p=0.043). In patients who didn’t experience seizures during follow-up, the hemosiderin ring was radically removed in 27 (71%) out of 38 cases, and in the group with unsatisfactory results, the hemosiderin ring was radically removed in only 1 (20%) out of 5 patients.
Gender, age, seizure types, and anatomical features of the CCM did not affect epilepsy outcomes in the postoperative period.
Conclusions: Surgical CCM resection is an effective method of treating CCM-associated epilepsy with low risks of surgical complications. Total excision of the hemosiderin ring around the CCM is a favorable prognostic factor for the patient's recovery from structural epilepsy when this pathology is present.
References
Rosenow F, Alonso-Vanegas MA, Baumgartner C, Blümcke I, Carreño M, Gizewski ER, et al. Cavernoma-related epilepsy: Review and recommendations for management - Report of the Surgical Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Vol. 54, Epilepsia. 2013. p. 2025–35.
Dammann P, Quesada CCM, Sato T, Sure U. Cavernoma-Related Epilepsy. In: Cavernomas of the CNS [Internet]. Springer, Cham; 2020 [cited 2022 Jun 24]. p. 103–14. Available from: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-49406-3_8
Kashida Y, Usui N, Matsuda K, Terada K, Baba K, Kondo A, et al. Is additional mesial temporal resection necessary for intractable epilepsy with cavernous malformations in the temporal neocortex? Epilepsy Behav [Internet]. 2019;92:145–53. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.12.024
Shang-Guan HC, Wu ZY, Yao P Sen, Chen GR, Zheng SF, Kang DZ. Is Extended Lesionectomy Needed for Patients with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations Presenting with Epilepsy? A Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018 Dec 1;120:e984–90.
Dammann P, Schaller C, Sure U. Should we resect peri-lesional hemosiderin deposits when performing lesionectomy in patients with cavernoma-related epilepsy (CRE)? Neurosurg Rev [Internet]. 2017;40(1):39–43. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0797-5
Okishev DN, Belousova OB, Shekhtman OD, Eliava SS, Sazonova OB, Kopachev DN. Amygdalohippocampectomy in treatment of epilepsy in patients with temporal lobe cavernomas. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2016;80(1):35–43.
Shan YZ, Fan XT, Meng L, An Y, Xu JK, Zhao GG. Treatment and outcome of epileptogenic temporal cavernous malformations. Chin Med J (Engl) [Internet]. 2015 Apr [cited 2020 Feb 3];128(7):909–13. Available from: http://insights.ovid.com/crossref?an=00029330-201504050-00010
Ruan D, Yu X-BB, Shrestha S, Wang L, Chen G. The role of hemosiderin excision in seizure outcome in cerebral cavernous malformation surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis [Internet]. PLoS ONE Public Library of Science; Aug 25, 2015 p. e0136619. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0136619
Vale FL, Vivas AC, Manwaring J, Schoenberg MR, Benbadis SR. Temporal lobe epilepsy and cavernous malformations: surgical strategies and long-term outcomes. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Internet]. 2015 Nov 29 [cited 2016 Nov 7];157(11):1887–95. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00701-015-2592-4
R Development Core Team. R Core Team (2023). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing_. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. R Found Stat Comput [Internet]. Available from: https://www.r-project.org/
Rinkel LA, Salman RAS, Rinkel GJE, Greving JP. Radiosurgical, neurosurgical, or no intervention for cerebral cavernous malformations: A decision analysis. Int J Stroke. 2019 Dec 1;14(9):939–45.
Ozlen F, Isler C, Akgun MY, Ozkara C, Karabacak M, Delil S, et al. Factors affecting seizure outcomes after surgery for cavernoma related epilepsy. Turk Neurosurg. 2021;32(3):0–3.
Baumann CR, Acciarri N, Bertalanffy H, Devinsky O, Elger CE, Lo Russo G, et al. Seizure Outcome after Resection of Supratentorial Cavernous Malformations: A Study of 168 Patients. Epilepsia [Internet]. 2007 Mar [cited 2023 Aug 20];48(3):559–63. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17346251/
Dziedzic TA, Koczyk K, Nowak A, Maj E, Marchel A. Long-Term Management of Seizures after Surgical Treatment of Supratentorial Cavernous Malformations: A Retrospective Single Centre Study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(3):415–21.
Schuss P, Marx J, Borger V, Brandecker S, Güresir Á, Hadjiathanasiou A, et al. Cavernoma-related epilepsy in cavernous malformations located within the temporal lobe: Surgical management and seizure outcome. Neurosurg Focus [Internet]. 2020 Apr 1 [cited 2023 Aug 12];48(4):E6. Available from: https://thejns.org/doi/abs/10.3171/2020.1.FOCUS19920
Dammann P, Wrede K, Jabbarli R, Neuschulte S, Menzler K, Zhu Y, et al. Outcome after conservative management or surgical treatment for new-onset epilepsy in cerebral cavernous malformation. J Neurosurg [Internet]. 2016 Jul [cited 2016 Nov 7];1–9. Available from: http://thejns.org/doi/10.3171/2016.4.JNS1661
Von Der Brelie C, Malter MP, Niehusmann P, Elger CE, Von Lehe M, Schramm J. Surgical management and long-term seizure outcome after epilepsy surgery for different types of epilepsy associated with cerebral cavernous malformations. Epilepsia. 2013;54(9):1699–706.
Harris L, Poorthuis MHF, Grover P, Kitchen N, Al-Shahi Salman R. Surgery for cerebral cavernous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev [Internet]. 2022 Feb 1 [cited 2023 May 19];45(1):231–41. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10143-021-01591-5
Kim DS, Park YG, Choi JU, Chung SS, Lee KC. An analysis of the natural history of cavernous malformations. Surg Neurol [Internet]. 1997 [cited 2023 Aug 12];48(1):9–17. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9199678/
Ferroli P, Casazza M, Marras C, Mendola C, Franzini A, Broggi G. Cerebral cavernomas and seizures: A retrospective study on 163 patients who underwent pure lesionectomy. Neurol Sci. 2006;26(6):390–4.
Wang X, Tao Z, You C, Li Q, Liu Y. Extended resection of hemosiderin fringe is better for seizure outcome: A study in patients with cavernous malformation associated with refractory epilepsy. Neurol India [Internet]. 2013 May [cited 2023 Aug 12];61(3):288. Available from: https://www.neurologyindia.com/article.asp?issn=0028-3886;year=2013;volume=61;issue=3;spage=288;epage=292;aulast=Wang
Williamson A, Patrylo PR, Lee S, Spencer DD. Physiology of human cortical neurons adjacent to cavernous malformations and tumors. Epilepsia [Internet]. 2003 Nov [cited 2023 Aug 12];44(11):1413–9. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14636349/
Jehi LE, Palmini A, Aryal U, Coras R, Paglioli E. Cerebral cavernous malformations in the setting of focal epilepsies: pathological findings, clinical characteristics, and surgical treatment principles. Acta Neuropathol [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 Aug 12];128(1):55–65. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24831066/
Chusid JG, Kopeloff LM. Epileptogenic effects of pure metals implanted in motor cortex of monkeys. J Appl Physiol [Internet]. 1962 Jul 1 [cited 2023 Aug 12];17(4):697–700. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13879433/
Lüders HO, Najm I, Nair D, Widdess-Walsh P, Bingman W. The epileptogenic zone: General principles. Epileptic Disord [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2023 Aug 12];8(SUPPL. 2):1–9. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17012067/
Baumann CR, Schuknecht B, Lo Russo G, Cossu M, Citterio A, Andermann F, et al. Seizure outcome after resection of cavernous malformations is better when surrounding hemosiderin-stained brain also is removed. Epilepsia [Internet]. 2006 Mar 1 [cited 2023 Aug 12];47(3):563–6. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00468.x
Wang S, Li Y, Xu Y, Song S, Lin R, Xu S, et al. Resection-inspired histopathological diagnosis of cerebral cavernous malformations using quantitative multiphoton microscopy. Issue 15 Theranostics [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Dec 26];2022(15):6595–610. Available from: https://www.thno.org//creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
Englot DJ, Han SJ, Lawton MT, Chang EF. Predictors of seizure freedom in the surgical treatment of supratentorial cavernous malformations: Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2011;115(6):1169–74.
Jin Y, Zhao C, Zhang S, Zhang X, Qiu Y, Jiang J. Seizure outcome after surgical resection of supratentorial cavernous malformations plus hemosiderin fringe in patients with short duration of epilepsy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg [Internet]. 2014;119:59–63. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.01.013
Zanello M, Goodden JR, Colle H, Wager M, Hamer PCDW, Smits A, et al. Predictors of Epileptic Seizures and Ability to Work in Supratentorial Cavernous Angioma Located Within Eloquent Brain Areas. Clin Neurosurg. 2019;85(4):E702–13.
Yeon JY, Kim JS, Choi SJ, Seo DW, Hong SB, Hong SC. Supratentorial cavernous angiomas presenting with seizures: Surgical outcomes in 60 consecutive patients. Seizure [Internet]. 2009 Jan 1 [cited 2023 Aug 19];18(1):14–20. Available from: http://www.seizure-journal.com/article/S1059131108001106/fulltext
Hammen T, Romstöck J, Dörfler A, Kerling F, Buchfelder M, Stefan H. Prediction of postoperative outcome with special respect to removal of hemosiderin fringe: A study in patients with cavernous haemangiomas associated with symptomatic epilepsy. Seizure [Internet]. 2007 Apr 1 [cited 2023 Aug 19];16(3):248–53. Available from: http://www.seizure-journal.com/article/S1059131107000027/fulltext
Cappabianca P, Alfieri A, Maiuri F, Mariniello G, Cirillo S, De Divitiis E. Supratentorial cavernous malformations and epilepsy: Seizure outcome after lesionectomy on a series of 35 patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1997 Aug 1;99(3):179–83.
He K, Jiang S, Song J, Wu Z, Chen L, Mao Y. Long-Term Outcomes of Surgical Treatment in 181 Patients with Supratentorial Cerebral Cavernous Malformation–Associated Epilepsy. World Neurosurg [Internet]. 2017;108:869–75. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.08.095
Fujimoto A;, Enoki H;, Hatano K;, Sato K;, Okanishi T, Fujimoto A, et al. Earlier Age at Surgery for Brain Cavernous Angioma-Related Epilepsy May Achieve Complete Seizure Freedom without Aid of Anti-Seizure Medication. Brain Sci 2022, Vol 12, Page 403 [Internet]. 2022 Mar 18 [cited 2022 Jun 24];12(3):403. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/12/3/403/htm
Kapadia M, Walwema M, Smith TR, Bellinski I, Batjer H, Getch C, et al. Seizure outcome in patients with cavernous malformation after early surgery. Epilepsy Behav [Internet]. 2021 Feb 1 [cited 2022 Jun 27];115:107662. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107662
Von Der Brelie C, Kuczaty S, Von Lehe M. Surgical management and long-term outcome of pediatric patients with different subtypes of epilepsy associated with cerebral cavernous malformations: Clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 Aug 21];13(6):699–705. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24702617/
Winter F, Blair L, Buchfelder M, Roessler K. Risk Factors for Poor Postoperative Outcome and Epileptic Symptoms in Patients Diagnosed with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. J Neurol Surgery, Part A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2021;82(1):59–63.
Casazza M, Broggi G, Franzini A, Avanzini G, Spreafico R, Bracchi M, et al. Supratentorial cavernous angiomas and epileptic seizures: Preoperative course and postoperative outcome. Neurosurgery [Internet]. 1996 Jul [cited 2023 Aug 26];39(1):26–34. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8805137/
Kivelev J, Niemelä M, Blomstedt G, Roivainen R, Lehecka M, Hernesniemi J. Microsurgical treatment of temporal lobe cavernomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011;153(2):261–70.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dmitry Galaktionov, Aleksey Sosnov, Konstantin Ovsyannikov, Elena Filimonova, Olga Subbotina, Evgeniya Amelina, Galina Moysak, Ekaterina Sorokoumova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain copyright of their work, with first publication rights granted to the publisher.


